Extract Using Search Engines
Use search engines to discover websites and extract email addresses automatically. Below are options, examples and tips to get better results.
Use this feature to find email addresses for people or organizations by entering one or more keyword(s). Click Start Search, enter keywords, and the program will query selected search engines (Google, Yahoo, Bing, and others) to find relevant pages — then automatically extract emails from them.
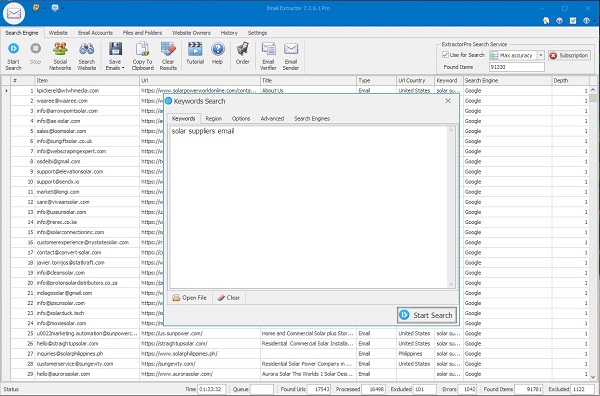
Search Options
Region
Choose Global search or limit results to a specific country to get more relevant local contacts.
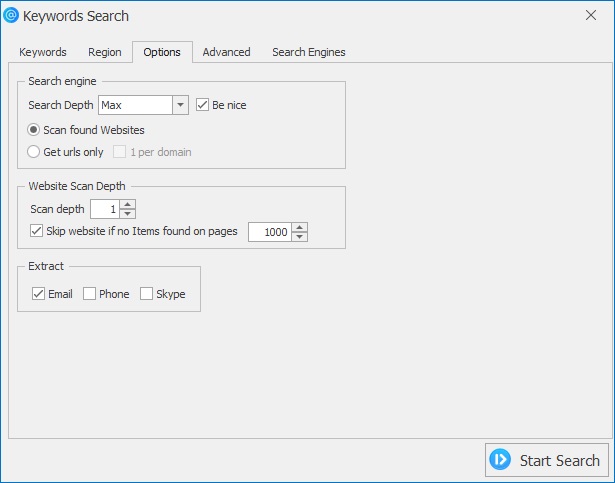
Basic Options
- Search depth: Number of search results requested from each engine (increase for broader coverage).
- Scan found website: After collecting URLs from search results, parse those sites for contact data.
- Get URLs only: Collect only URLs without downloading page content (fast, useful for later batch crawling).
- Scan depth: How many link levels to follow on a site (Level 1 = page only; Level 2 = page + linked pages, etc.).
- Extract fields: Select which contact details to collect — Email, Phone, Skype, Social links, etc.
Advanced Options
- Only this domain: Restrict parsing to the original domain returned by the search engine (avoids external links).
- Improved Page Loading: Loads pages using the embedded browser to render JavaScript-heavy sites — useful for a few important sites (use sparingly for large-scale searches).
- Human emulation: Simulates human browsing (delays, scrolling, JS execution) to reduce blocking by anti-bot systems and to load dynamic content.
- Follow redirects: Enable to correctly handle sites that redirect to different domains or country mirrors.
- Proxy support: Use proxies for high-volume scraping or to access region-restricted results.
Social Networks
Many contacts appear on social network profiles (LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter). Use targeted queries such as site:linkedin.com "email" or include social-network-specific operators. Note that scraping some social networks may violate their terms — always check and respect the network's rules.
- LinkedIn: Use company pages and people profiles — often emails are not public but can be found in exported files or personal sites linked on profiles.
- Twitter / Facebook: Search for «contact», «email», or pages with «contact us» sections.
Search in Website
To focus on a single website, use the search operator for site-scoped queries (e.g., site:example.com email), or add the website URL directly into the extractor's Website mode. Choose an appropriate scan depth depending on site size.
Tip: For large domains, start with Level 1 or Level 2 to avoid long crawls; then run Deep mode on promising subdomains or sections.
Search Examples
Copy / paste these example queries into the keyword field to test the extractor:
Basic company search
"contact" inurl:companyname
Niche + email
email inurl:startup "angel investor"
Find site contacts
site:example.com "contact" OR "email"
Exclude terms
"email" -job -careers
Pro tip: combine operators for precision (quotes for exact match, minus to exclude terms, site: to limit the domain).
Saving Results
After extraction you can inspect results in the Results pane. To save:
- Click Save Emails on the toolbar.
- Choose fields to include (Email, Source URL, Page Title, Phone).
- Select export format: .txt, .lst, .csv, or .xlsx (export available in registered version).
- Click Save and choose the folder to store the file.